TL;DR: Geofencing can be a valid protection mechanism when facing current hacktivism-threats and botnet-attacks, but shouldnt be the only option you have. And if you operate international / beyond single countries, this options becomes more difficult.
Also, some bad guys already know how to mitigate your mitigation
Introduction
In recent years, the threat landscape has witnessed a significant rise in Layer 7 DDoS attacks orchestrated by hacktivist groups. These attacks target the application layer of web services, aiming to overwhelm servers and disrupt the normal functioning of targeted organizations. In response to this evolving threat, geofencing or GeoIP blocking has emerged as a valuable protection strategy. This article explores how geofencing can effectively mitigate the risks posed by such attacks and enhance overall security posture.
Understanding Layer 7 DDoS Attacks
Layer 7 DDoS attacks differ from traditional volumetric attacks by specifically targeting the application layer of a network. They exploit vulnerabilities in web applications, overwhelming servers with malicious traffic that mimics legitimate user requests. These attacks often result in service disruptions, unauthorized access, or data breaches. The motive behind these attacks varies, with hacktivist groups seeking to achieve socio-political goals or make public statements.
The Importance of Geofencing
Geofencing, a technique used to restrict network traffic based on the geographical location of IP addresses, has proven to be an effective defense mechanism against Layer 7 DDoS attacks. By implementing geofencing measures, organizations can block traffic originating from specific countries or regions that are known to be associated with hacktivist activities. This strategy minimizes the attack surface and reduces the potential impact of these attacks.
Geofencing used in recent Attacks
We have seen geofencing actively used in a lot of recent hacktivism-driven attacks against institutions all over europe, where the blueteamers learned this effective technique very fast
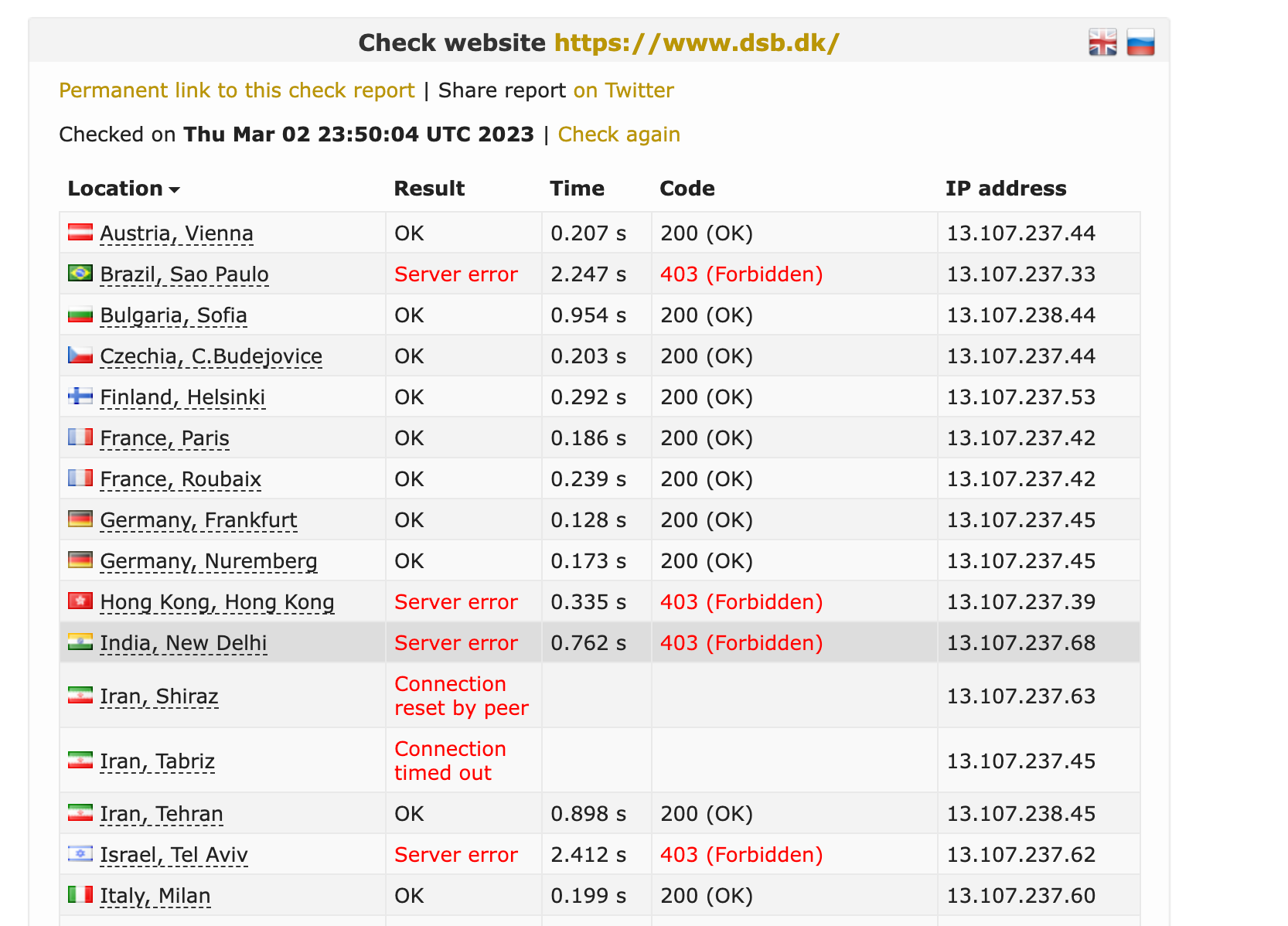
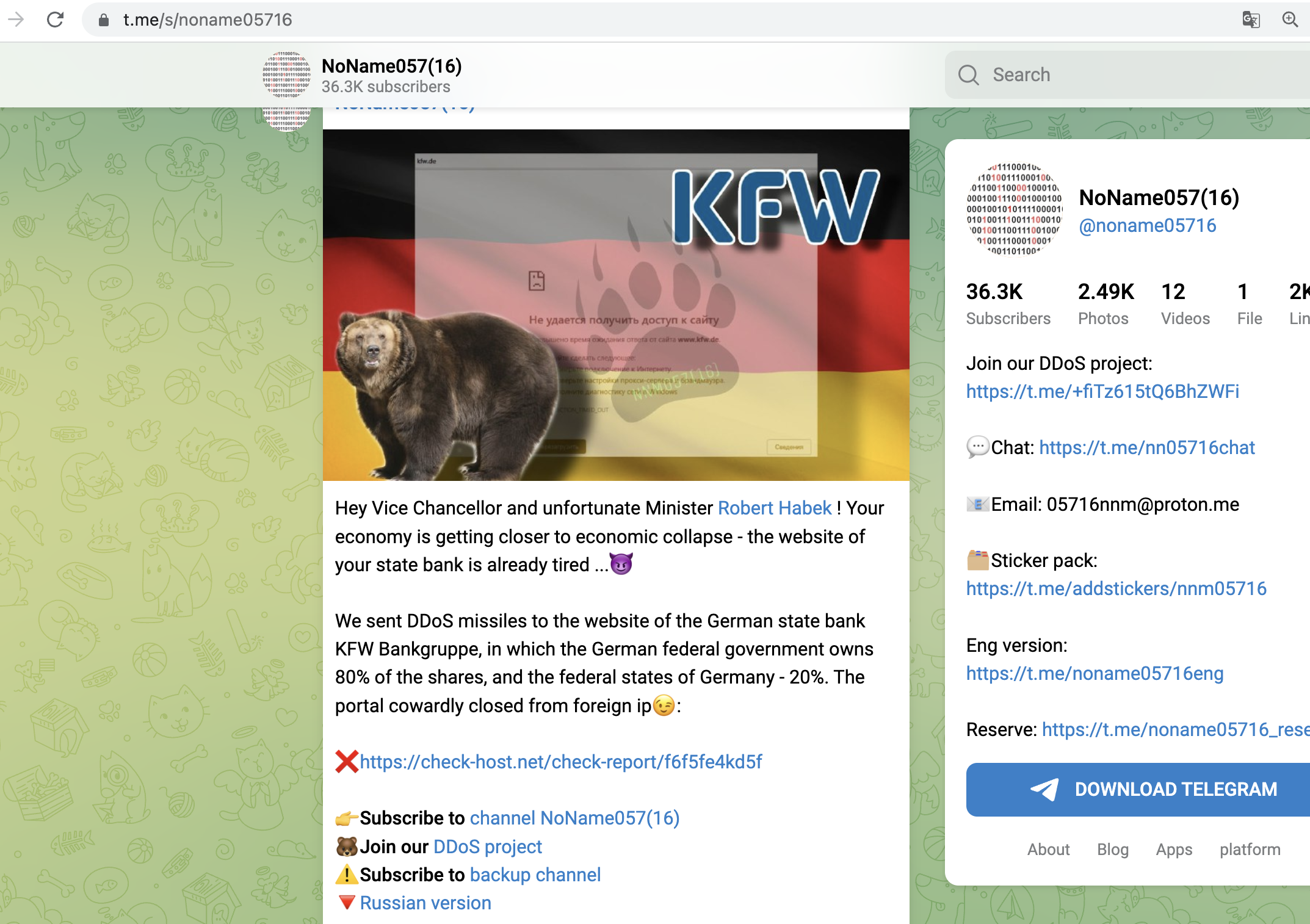
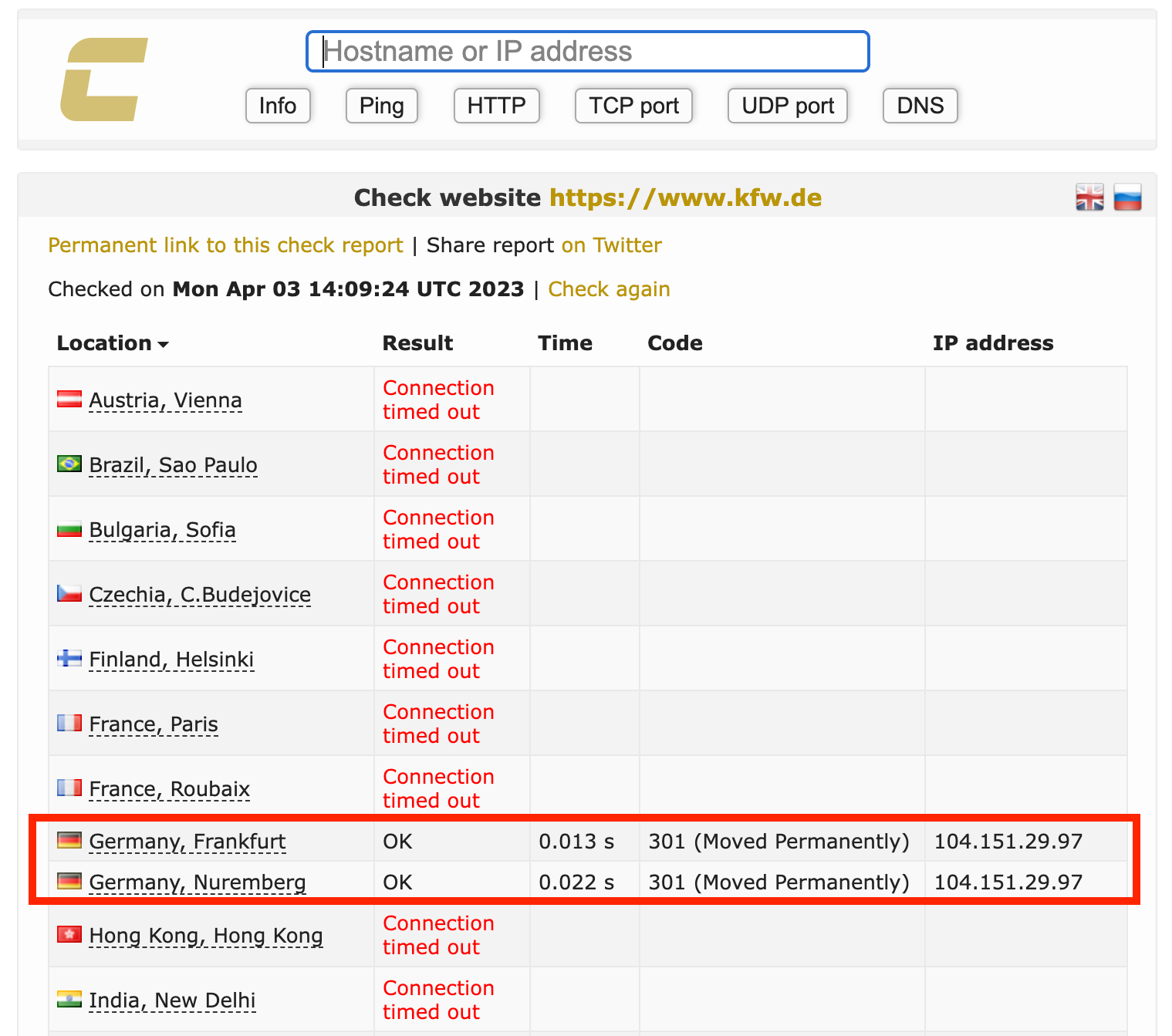
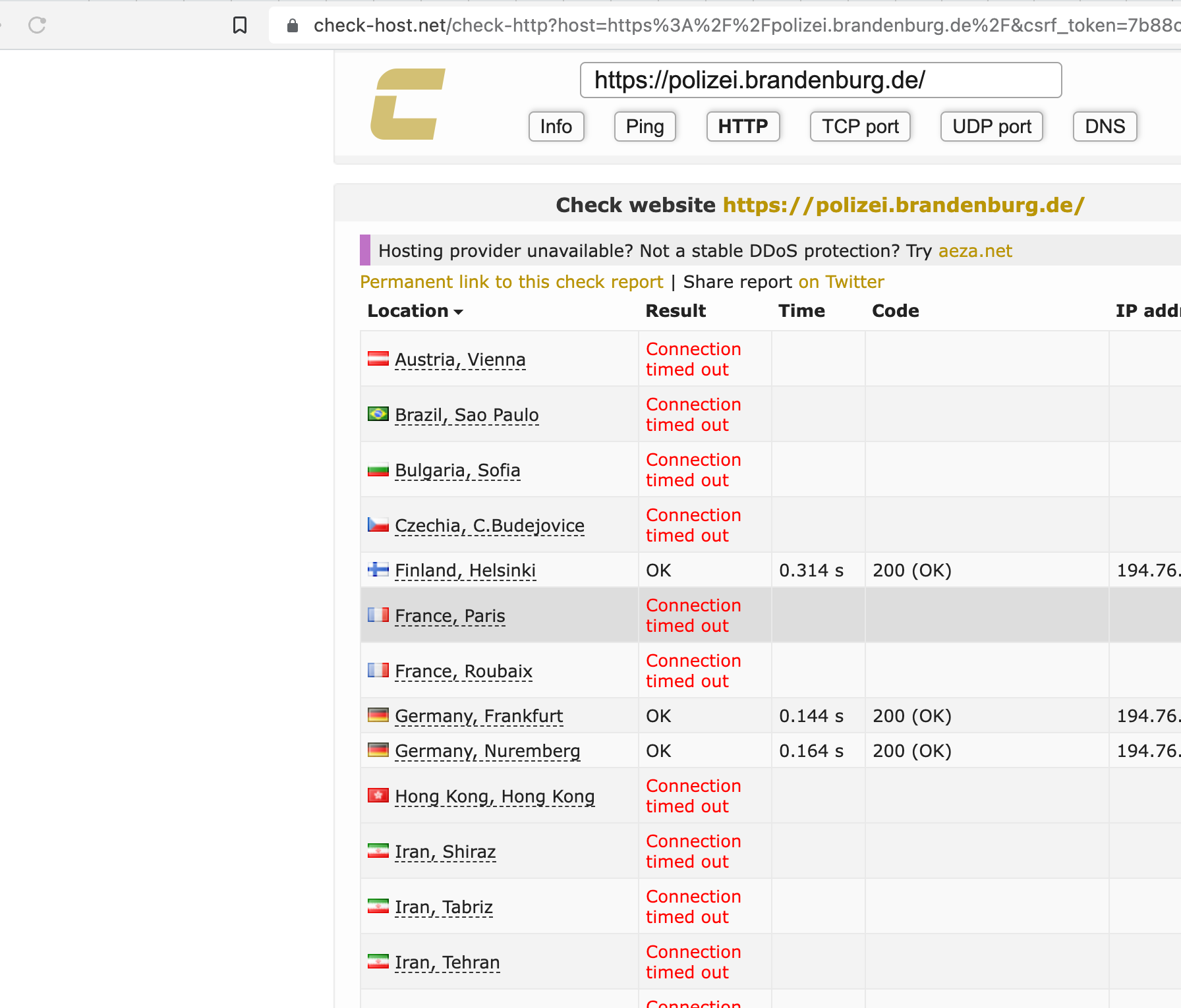
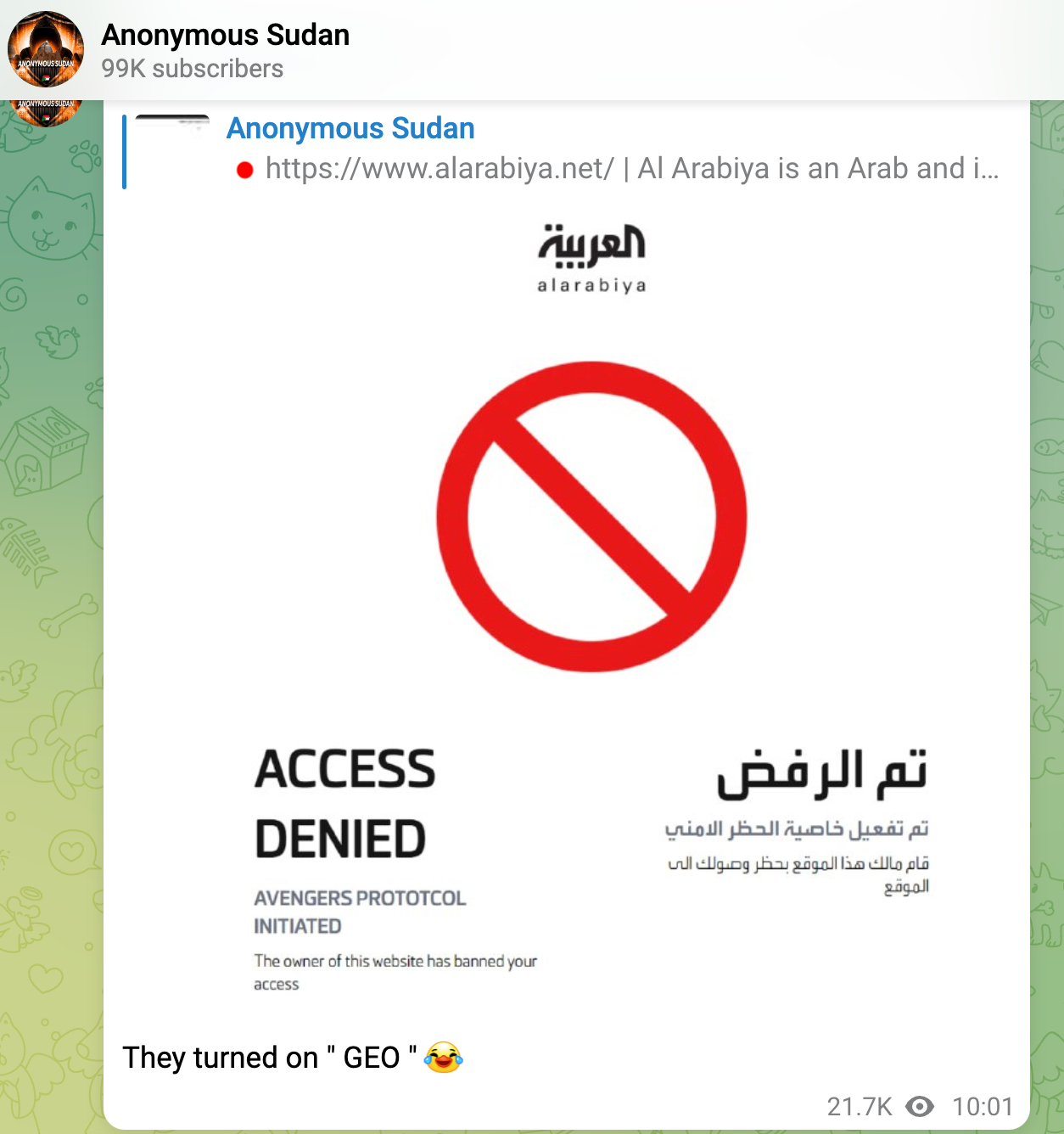
Considerations and Best Practices:
While geofencing can be an effective strategy, it is important to consider the following best practices:
- Accurate Geolocation Data: Geofencing relies on accurate geolocation data to identify and block traffic from specific regions. It is crucial to use reliable data sources and keep the geolocation database up to date to avoid false positives or false negatives.
- Blacklisting vs Whitelisting: if you operate in a single country or Region, you might be able to apply a pure whitelisting-approach in times of an attack, allowing only Users from certain Countries or Regions. If you are an international organization you might want to consider to blacklist certain countries, but in order to do so, you MUST be able to analyze where the attack originates from. Whitelisiting is more comfortable, but not always possible.
- Fine-Tuned Policies: Organizations should tailor geofencing policies based on their specific needs and risk profile. This includes identifying regions with a high frequency of hacktivist activities and adjusting blocking rules accordingly.
- Monitoring and Adaptation: Continuous monitoring of network traffic patterns and attack trends is essential. It allows organizations to adapt geofencing policies based on emerging threats and changing attack patterns.
Conclusion
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, layer 7 DDoS attacks by hacktivist groups pose significant challenges for organizations. Geofencing provides an effective defense mechanism, allowing organizations to proactively mitigate risks by blocking traffic from high-risk regions. By implementing geofencing measures alongside other security strategies, organizations can bolster their resilience against these attacks and ensure the uninterrupted operation of their critical web services.

Member discussion: